- How To Use The Ipconfig Command - Windows 10 - 2021
- Ipconfig Not Working
- Ipconfig - IP Location
- The Complete List Of Windows Commands
- See Full List On Docs.microsoft.com
- Ipconfig Mac
The result of ipconfig command shows that the IP 169.254.29.130 with the mask of 255.255.255.0 is my current Windows IP address. This is a class C “autoconfiguration IPv4”. When your system doesn’t find any DHCP Server or manual IP address, it obtains auto IP address.
The ipconfig (short for IP Configuration) is a basic, yet popular, Windows network command-line utility used to display the TCP/IP network configuration of a computer. If you are familiar with Linux, this tool is similiar to ifconfig. This tool is often used for troubleshooting network connectivity issues. With ipconfig, you can identify the types of network adapaters on your computer, the computer's IP address, the IP addresses of the DNS (Domain Name System) servers being used, and much more.
These commands shown here are tested on a comptuer with Windows 10 but most will work in other versions of Windows as well.
Table of Content
- Example Usage
- ipconfig - Retrieves Basic TCP/IP Network Information (IP, subnet mask, gateway)
- ipconfig /all - Retrieves All TCP/IP Network Information (MAC address, adapter description, DHCP details)
- ipconfig /release - Releases the IPv4 Address of All Network Adapters
- ipconfig /release6 - Releases the IPv6 Address of All Network Adapters
- ipconfig /release <adapter> - Releases the IP Address of a Specific Network Adapter
- ipconfig /renew - Get a New IPv4 Address for All Network Adapters
- ipconfig /renew6 - Get a New IPv6 Address for All Network Adapters
- ipconfig /renew <adapter> - Get a New IPv4 Address for a Specific Network Adapter
- ipconfig /displaydns - View DNS Cache
- ipconfig /flushdns - Purge DNS Cache
- ipconfig /all | findstr /v 00-00-00 | findstr Physical - Display MAC Address of Only Physical Connected Network Adapters
- Tips
Ipconfig /release6: Same as above but for the IPv6 address. Ipconfig /renew: This usually comes after the above command and is used to request a new IP address from a DHCP server. Ipconfig /renew6: Same as above but for the IPv6 address. Ipconfig /flushdns: This deletes the local DNS resolver cache of the computer. This cache stores DNS. Type ipconfig and press enter. Or ipconfig /all to view IP addresses assigned to all the Network Interface Cards. You’ll see a bunch of information, but the line you want to look for is “IPv4 Address.” The number across from that text is your local IP address. Below is an example image. Dec 15, 2020 Viewing Basic IP and DNS Settings with IPConfig Commands The most basic of ipconfig commands is simply running it without parameters. Open up a command prompt or PowerShell console on your machine and run ipconfig. You will see all of the network interfaces (NICs) installed on your system along with basic IP information. Displays all current TCP/IP network configuration values and refreshes Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS) settings. Used without parameters, ipconfig displays Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) and IPv6 addresses, subnet mask, and default gateway for all adapters.
Overview
The ipconfig is a Windows command-line utility used often to troubleshooting computer network issues. If you are a Linux user, this utility is similar to ifconfig. This is often used to determine the local IP address, subnet mask, the gateway address, and other network configuration of a computer. Additionally, this tool is used to refresh DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) and DNS (Domain Name System) settings
While most of the information provided by the ipconfig command-line utility can be found via a more user-friendly graphical interface, sometimes that interface may not be available and command prompt is your only available option. If you are a help desk technician or a network professional, it is recommended that you understand the command-line method of retrieving a computer's network configuration, and it some cases, performing network functions.
How to Open Command Prompt
To use this utility, you will need to launch the Command Prompt window. The three common ways to launch the Command Prompt window are:
- Search for
cmdusing the built-in Windows search tool. - Right-click on the Start icon and select Command Prompt.
- Press the keyboard combination WinKey + R, then type
cmdat the Run window that appears.
Ipconfig Syntax
ipconfig [/allcompartments] [/all] [/renew [<Adapter>]] [/release [<Adapter>]] [/renew6[<Adapter>]] [/release6 [<Adapter>]] [/flushdns] [/displaydns] [/registerdns] [/showclassid <Adapter>] [/setclassid <Adapter> [<ClassID>]]>Ipconfig Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| /all | Display the full TCP/IP configuration information for all network adapters. |
| /release | Release the IPv4 address for the specified adapter. |
| /release6 | Release the IPv6 address for the specified adapter. |
| /renew | Renew the IPv4 address for the specified adapter. |
| /renew6 | Renew the IPv6 address for the specified adapter. |
| /flushdns | Purges the DNS Resolver cache. |
| /registerdns | Refreshes all DHCP leases and re-registers DNS names. |
| /displaydns | Display the contents of the DNS Resolver Cache. |
| /showclassid | Displays all the DHCP class IDs allowed for adapter. |
| /setclassid | Modifies the DHCP class ID. |
| /showclassid6 | Displays all the IPv6 DHCP class IDs allowed for adapter. |
| /setclassid6 | Modifies the IPv6 DHCP class ID. |
| /? | Displays help information. |
Example Usage
There are a variety of switches (sub commands) available with the ipconfig utility that will either display certain information or perform certain network functions. At the most basic, the ipconfig displays a computer's IP address, subnet mask and the default gateway (which is typically the IP address of your router or network firewall). Bluestacks 4 mac os download.
ipconfig - Retrieve Basic TCP/IP Network Information
To get basic network information from your computer, type the following in the command window then press Enter: ipconfig
The screenshot example below is the ipconfig output of a particular computer. The output of your ipconfig result will differ depending on your network setup and the type of network adapters installed on your computer. In our screenshot example, it shows the following basic networking information about the computer from which ipconfig was ran.
- IPv4 address: 192.168.0.98
- Network subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
- Default Gateway: 192.168.0.1
Please note that unless your computer is connected directly to the Internet (this is rare), the IP address reported by ipconfig will be your local network IP, not your public external IP address.
While other network details can be retrieved by the ipconfig utility, for most network troubleshooting, this is what is typically needed.
Back to Topipconfig /all - Retrieve All TCP/IP Network Information
Another useful switch with ipconfig is to have it report all TCP/IP network details for all network adapters on a computer. This is accomplished by using the /all switch. This switch provides you with the same basic information as ipconfig described above, but with a lot more detail. To retrieve all network information about your computer, type the following in the command window then press Enter: ipconfig /all
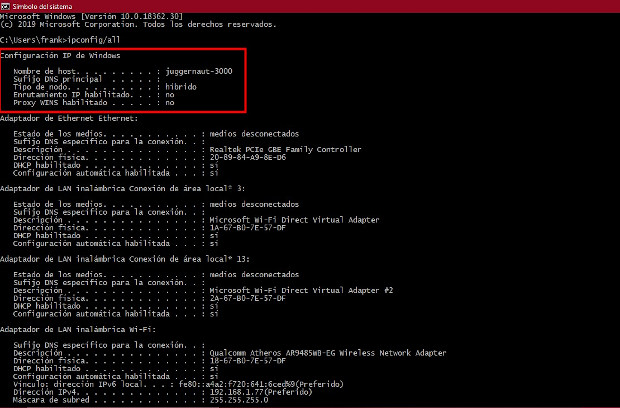
This will show a detailed report of various network details for the computer. Again, your report will differ depending on your network setup and the network adapters installed on your computer. This report includes information such as:
- Make and model of your network adapter(s)
- Physical address (also known as the MAC address or hardware address) of your adapter(s)
- Whether your IP address is leased (i.e., DHCP issued or statically assigned)
- If IP address is leased, what the lease expiration and the DHCP that leased it
- DNS servers
As you can see, ipconfig /all provides you with a plethora of details about your computer network setup.
MAC Address (OUI) Lookup Tool
A MAC address is made up of six (6) octets. The first three octets indicate the manufacturer of the network adapter. Use this MAC Address (OUI) Lookup Tool to find the manufacturer of your adapter.
ipconfig /release - Releases the IPv4 Address of All Network Adapters
The /release switch will cause ipconfig to go through the network adapters you have and drop the dynamically issued IPv4 address by sending a DHCPRELEASE message to the DHCP server. For the majority of the time, you would follow this command with ipconfig /renew (described below) will cause your network adapters to reach out to your DHCP server for an IP address (it can be a new IP address or the same IP you had prior to when you performed the /release command). For most, executing this command does not have adverse effect on your computer.
To release your IP address from your computer, type the following in the command window then press Enter: ipconfig /release
Note, if you have a statically assigned (manually assigned) IP address, this command will not release it. See example ipconfig /renew for related information.
ipconfig /release6 - Releases the IPv6 Address of All Network Adapters
The command is similar to ipconfig /release except it renews the IPv6 address on the adapters.
ipconfig /release <adapter> - Releases the IPv4 Address for a Specific Network Adapters
The /release <adapter> switch will cause ipconfig to drop the dynamically issued IPv4 address by sending a DHCPRELEASE message to the DHCP server for a specific network adapter.
To release the IP address for a specific network adapter on your computer named 'Local Area Connection 3', type the following in the command window then press Enter: ipconfig /release 'Local Area Connection 3'
Note, if you have a statically assigned (manually assigned) IP address, this command will not release it. See example for ipconfig /renew for related information.
ipconfig /renew - Get a New IPv4 Address for All Network Adapters

The ipconfig /renew will cause your computer to reach out to your DHCP server for an IPv4 address if it doesn't already have one or renews an existing one for all network adapters. Depending on how your DHCP server is configured or the pool of available addresses, the IP address you will receive can be one you had previously or it can be a new IP address. Once you execute this command, it will typically take just seconds for a DHCP to assign your computer with an IP address. In the illustration below, the IP address assigned to this computer is 192.168.226.132.
To renew the IP address of your computer, type the following in the command window then press Enter: ipconfig /renew
See example for ipconfig /release for related information.
ipconfig /renew6 - Get a New IPv6 Address for All Network Adapters
How To Use The Ipconfig Command - Windows 10 - 2021
The command is similar to ipconfig /renew except it renews the IPv6 address on the adapters.
ipconfig /renew <adapter> - Get a New IPv4 Address For a Specific Network Adapter
The ipconfig /renew <adapter> will cause your computer to reach out to your DHCP server for an IPv4 address if it doesn't already have one or renews an existing one for a specific network adapter. Depending on how your DHCP server is configured or the pool of available addresses, the IP address you will receive can be one you had previously or it can be a new IP address. Once you execute this command, it will typically take just seconds for a DHCP to assign your computer with an IP address. In the illustration below, the IP address assigned to the network adapter named 'Local Area Connection 3' is 192.168.226.132.
To renew the IP address for a network adapter on your computer named 'Local Area Connection 3', type the following in the command window then press Enter: ipconfig /renew 'Local Area Connection 3'. To find out the name(s) of the network adapters on your computer, type the following in the command window then press Enter: ipconfig
See example for ipconfig /release for related information.
ipconfig /all | findstr /v 00-00-00 | findstr Physical- Display MAC Address of Only Physical Connected Network Adapters
The ipconfig utility, with the /all switch, is often used to find the MAC address (the 6-byte 'burned-in' physical/hardware address) of network adapters. While this does the job, the output shows a plethora of information as mentioned above. If you have multiple adapters, the output can be lengthy making it cumbersome to find what you are looking for.
The Windows findstr utility is used to search for patterns of text. By feeding the output of ipconfig /all into findstr, we can significantly reduce the clutter and have the output show only the MAC address of physical network adapters. To accomplish this, type the following in the command window then press Enter:
ipconfig /all | findstr /v 00-00-00 | findstr Physical
This command is actually a series of three commands, namely:
ipconfig /allfindstr /v 00-00-00findstr Physical
The vertical bar (|), more commonly referred to as the pipe, is a 'command' that takes the output from the left side of the pipe and feeds it as input to the command on the right, bypassing the computer screen.
As the above command shows, the output of ipconfig /all is funneled into the command findstr /v 00-00-00 as its input. The findstr with the /v switch will look for lines of text in the output of ipconfig /all that does not contain 00-00-00. What this does is exclude any network adapters that are disabled or not connected. These network adapters will have MAC address that starts with 00-00-00.
The result from the first findstr will still contain a lot of information that we can further filter out, such as DHCP lease information. To further reduce clutter to ultimately end up with an output that lists only MAC address of physical adapters, we will need to funneled the output of the first findstr into a second findstr command. This second findster will filter out every line of text except those that has the word Physical.
This series of commands produce an output that is concise to show only the MAC address of connected network adapters. As the illustration below shows, this is a much more easier report to read as oppose to using just using ipconfig /all.
ipconfig /displaydns - View DNS Cache
When you visit a website using it's domain name (e.g., www.meridianoutpost.com), your computer will need to know the IP address for that website in order for it to find it the server hosting it on the Internet. The process of identifying the IP address is called DNS lookup (analogous to looking up a number in a phone book). Once your computer learns the associated IP address for the website you want to visit, it will cache it (store it) on your computer. The purpose of caching it is to improve performance by not having your computer perform a DNS lookup each time you access a web page on the website.
This command will list all the currently cached IP addresses on your computer (also referred to as the DNS resolver cache). If you've accessed a lot of websites since turning on your computer, this list can be very lengthy. The illustration below shows just a few entries out of many for a particular computer. If you just turned on our computer and have not access websites or servers on the network on the Internet, then you list will only show a 'localhost' setting in your local hosts file.
To display cached DNS entries on your computer, type the following in the command window then press Enter: ipconfig /displaydns
This command is typically used to troubleshoot specific DNS lookup issues. See example for ipconfig /flushdns for related information.
The information displayed on the list include:
- Record Name: the name of the website or server that a DNS lookup was performed on
- Record Type:
- 1 = A
- 2 = NS (indicates the entry is a name server)
- 5 = CNAME (stands for canonical name and is a type of record that maps an alias name to a true domain name)
- 15 = MX (indicates the entry is an email server)
- Time to Live: the time (in seconds) before this cache entry expires (can be as short as a few minutes to a few days)
- Data Length: the length (in bytes)
- 8 Bytes = IPv4 address
- 16 Bytes = IPv6 address
ipconfig /flushdns - Purge DNS Cache
This command will purge the cached DNS entries on your computer. You would typically do this to troubleshoot DNS related problems. An example of this is when you try to access a website but you encounter an error message stating the website is not found. For most people, executing this command does not have adverse effect on your computer. See example for ipconfig /displaydns for related information.
To delete all the cached DNS entries on your computer, type the following in the command window then press Enter: ipconfig /flushdns
Other Usages and Getting Help
The example usage described in the article shows only some of the functions available with ipconfig. To get a list of the available switches, type the following in the command window then press Enter: ipconfig /?
Tips
Redirect Output to Text File
- Instead of displaying the results on the screen, you can have the results saved automatically to a text file on your computer. To do this, simply use the '>' symbol followed by the folder path and file name of your choice. For example, to redirect the output of ipconfig /renew, type the following in the command window then press Enter:
ipconfig /renew > c:tempipconfig-results.txt
This will create a file named ipconfig-results.txt in the folder path c:temp that will have your result. You can then open this file with any text editor, such as Notepad on a Windows computer, as illustrated below.
Recommended Reading
Improve productivity and efficiency
Life-long
investment
Ipconfig Not Working
To learn more about this topic, we are providing you with recommendations to help you further your knowledge. These are our affiliate links to Amazon where you can purchase them and also explore a variety of other relevant books.An investment in knowledge always pays the best interest.
ipconfig command provides basic network management functionalities about Windows operating systems like Windows Server and Windows Desktop families. With ipconfig command IP address information about network interfaces can be listed, changed or DNS cache can be flushed. In this tutorial, we will look at these usage examples.
ipconfig Command Help
Ipconfig command uses default Windows-style parameters and syntax for help information. We will use /h for print help. We can see that help provides useful information with the provided options and their functions.
All parameters about the command ipconfig are provided with the help information. Also, some short description of these options is listed. Below we will list all parameters and their description provided by ipconfig command.
/all displays TCP/IP full configuration information.
/displaydns displays the contents of the DNS client resolver cache.
/flushdns flushes and resets the contents of the DNS client resolver cache.
/registerdns initiates manual registration for the DNS names and IP addresses that are configured at a computer.
/release releases IPV4 IP addresses with DHCPRELEASE message.

/release6 releases IPv6 IP addresses.
/renew renews DHCP configuration for all adapters or specific adapter if specified.
/renew6 renews DHCPv6 configuration for all adapters or specific adapter if specified.
/setclassid configures the DHCP class ID for specific adapter.
/showclassid displays the DHCP class ID for specified adapter.
/? or /h prints help information about ipconfig command parameters.
List All Network Interfaces and IP Addresses
Windows operating systems have more than one interface. These interfaces have information like IP, DNS, Network, etc. We can display this information with ipconfig command without providing any parameters. This will list all interfaces and related information.
We can see that there are the following information;
- Interfaces name is the name of the given adapter in a human-readable form. In this example, it is named as
Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection - IPv4 Address is the IP address of the given network interface in version 4. In this example, IPv4 address is
192.168.122.1 - Subnet Mask is the value used to calculate network address which is
255.255.255.0in this case - Default Gateway is the IP address of the network gateway where communication can be done outside of the network. In this example, the default gateway address is
192.168.122.1 - Link-local IPv6 Address is the IP address in version 6.
List DNS, DHCP Server and Detailed Information
In the previous example, we have listed basic information about network interfaces. Some times this information is not enough for us. We need more detailed information like DHCP Server, DNS Server, etc. We can get these details with /all parameter.
Ipconfig - IP Location
We can see that all the information about network, NIC, DHCP is provided in this case.
Lease Obtainedprovides the date the IP address is obtained from the DHCP server which isFriday March 31 , 2017 05:08:04 AMin this caseLease Expiresprovides the date where the IP lease will be expired. Before this date, the IP lease should be renewed in order to continue to use it. In this case, the lease expire date isFriday March 31 , 2017 07:59:35 AMDHCP Serveris the DHCP server IP address which is192.168.122.1DNS Serveris the DNS server IP address which is192.168.122.1
Renew IP Address
DHCP is a protocol used to get an IP address and other related network information automatically. DHCP ease system and network administrators life. DHCP protocol details can get from the following tutorial
DHCP mechanism started d by client-side or a network node generally connected newly. Ipconfig command can start this mechanism with /renew parameter. We will release our IP address if already exists and try to get a new IP address in the following example.
The Complete List Of Windows Commands
Renew IP Address of Specified Network Interface
We have the option to renew the IP address of a specific Network Interface. We need to provide the whole network interface name or some part of the name with glob prefix and postfix. In this example, we will renew the IP address of interface which name contains Con in some part of its name.
See Full List On Docs.microsoft.com
As another example, we can renew the IP address of the network interface which is named as Ethernet Adapter Local Area Connection like below.
Clear DNS Cache with ipconfig Command
Ipconfig Mac
One of the most faced network problems is a DNS problem. After some times using internet connection DNS cache became corrupt and can not work properly. we can connect network by can not surf the internet or get a DNS related error from the browser like Chrome, Firefox, Explorer we can try to clear DNS cache. We will clear the DNS cache with /flushdns parameter like below.